
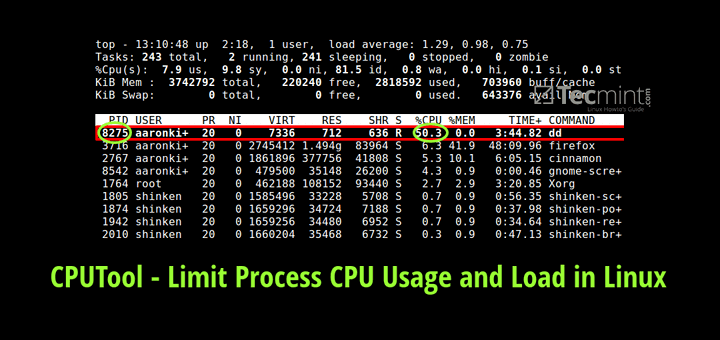

In our previous example, we would have one-minute load times of. A completely idle processor would have a load value of 0. Instead of measuring the percentage of time that the CPU is working, CPU load measures how many programs are using or waiting for a processor core at one time. You could downgrade your processor to a lower tier, save money, and see no reduction in the quality of your server’s performance. Most servers are sold by overall computing power, and if your server is only sitting at 30% CPU usage, you’re paying for too much processor power. Most companies seek to keep the CPU usage of their servers as close to 100% as possible. Instead, if the program only required six seconds processing time on one core, the usage would be 10%. For instance, if you had a program that required uninterrupted processing power for 54 out of the last 60 seconds, your CPU usage on one core would be 90%. CPU usage is a measurement, in a percentage, of how much time the CPU spends actively computing something.
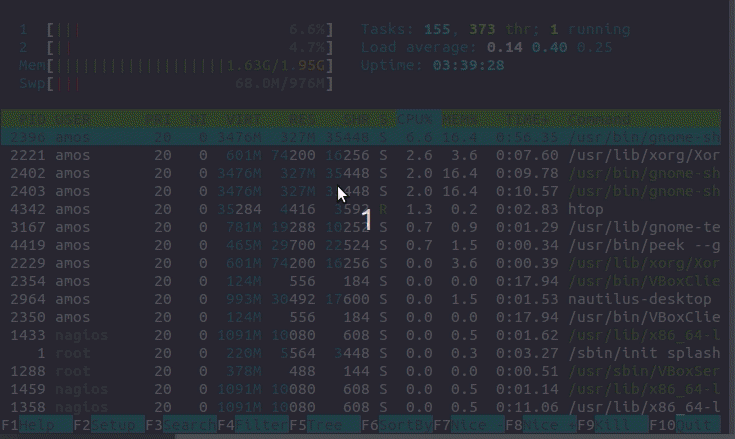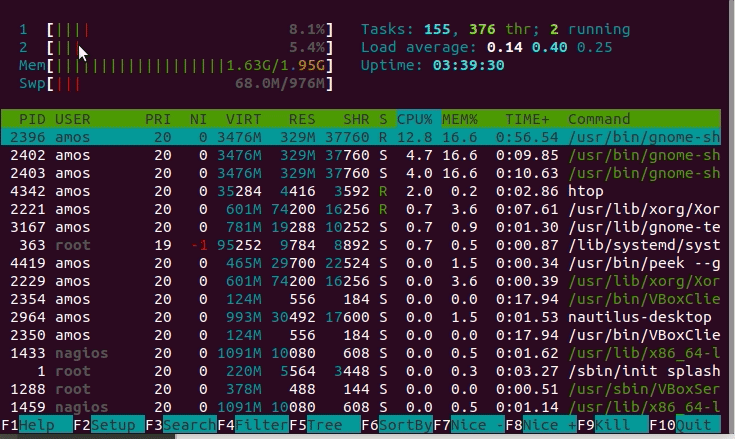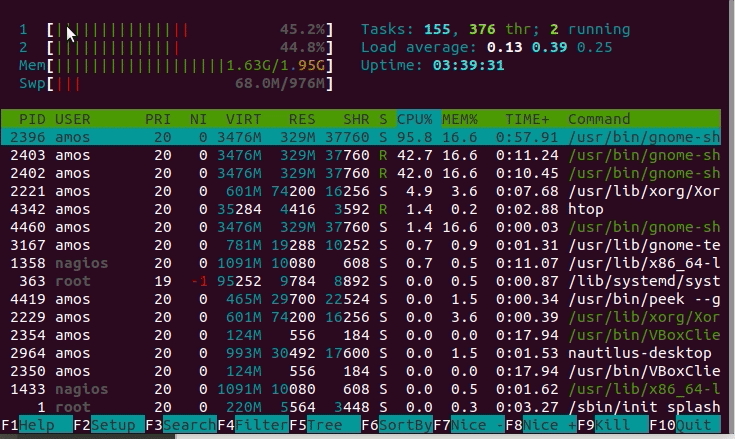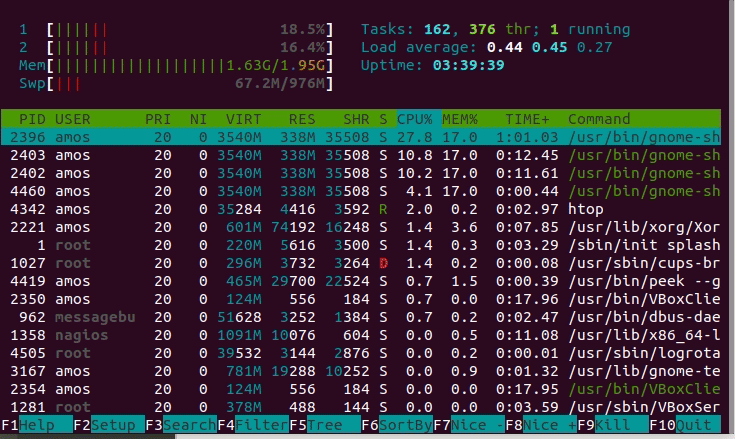
Even though they might sound similar, they’re quite different. The best way to install the htop is using snap because it works well on any of the Linux distros.The first thing to understand is that CPU load is not the same thing as CPU usage. In most of the distros, the top is installed by default, and we have to install the htop manually. In this, we can also scroll horizontal as well as vertical. As compared to the top, the htop UI has better quality. The htop's default display is more user-friendly. On the other hand, the htop command offers a better quality-of-life experience. In terms of system monitoring both commands offer the same functionality. st: st is the time lost for running a virtual machine, which is also called "steal time.".si: si is the time spent servicing software interrupts.hi: hi is the time spent servicing hardware interrupts.wa: wa means the amount of time spent waiting for I/O request to complete.ni: ni is the time spent to run the process with a custom (manually set) excellent value.sy: sy is the time spent running "kernel space" processes.us: The amount of time it takes to run the process for individual users in the "user space.".Each value indicates how much time the CPU spends performing a task. In the above output, the main line to focus on is the line number third.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
